Determine the Products Formed in Each Reaction
Solution for Determine the products that form in the double displacement reaction between each pair of reactants. A hydrocarbon and oxygen O 2 indicate a combustion reaction.

Stereospecificity Of E2 Elimination Reactions Practice Problems Reactions Chemistry How To Know
A precipitation reaction refers to the formation of an insoluble salt when two solutions containing soluble salts are combined.

. Then write a balanced chemical equation for. The mole ratios between each reactant and the product are needed to complete the calculation. AB A B decomposition c.
Up to 256 cash back For each reaction calculate the mass in grams of the product formed when 105 g of the underlined reactant completely reacts. Of the underlined reactant completely reacts Assume that there is more than enough of the other reactant. When you have predicted the products balance the equation and use a table of solubility products to determine which of the products if any will precipitate.
Assume that there is more than enough of the other reactant. For every one mole of O 2 two moles of H 2 O are produced. Molar mass of H 2 2 grams molar mass of O 2 32 grams molar mass of H.
For example an unsolved and unbalanced equation. 1 NacECH 2 H20 1 CH3MgBr 2 H2o 1 CGHsLi 2 H2O I CH32CuLi 2 H20 2 H20. Determine the product formed when butanone CH3CH2COCH3 is treated with each reagent.
C When the reaction proceeds G c absorption at 1650 c m 1 once the. Stoichiometric ratios the ratios of the amounts of each substance used are unique for each chemical reaction. Solution for For each reaction calculate how many moles of the product form when 0112 mol of the reactant in color completely re- acts.
Change in concentration is calculated using A final A initial and. Precipitation reactions can help determine the presence of various ions in solution. For unlimited access to Homework Help a Homework subscription is required.
See Sample Problem G. Up to 256 cash back Chemistry. Learning Objectives Determine the limiting reagent and the amount of a product formed in a given reavion.
Each product has a theoretical yield meaning the amount of product you would expect to get if the reaction is perfectly efficient. Carbon-Carbon BondForming Reactions in Organic Synthesis. If it is combustion then just write H 2O and CO 2 as products.
The coefficients of each product if the reaction is balanced tells you the amount to expect in molecular ratios. 2H2gO2g 2H2Og 2 H 2 g O 2 g 2 H 2 O g There is a clear relationship between O 2 and H 2 O. Assume all reactions take place in water.
1 1Ca OH22HF 2 H2O CaF2CaF2precipitates 2 1Pb NO32 1K2CrO4 2 KNO3 PbCrO4PbCrO4precipitates 3 2NaC2H3O2 1H2SO4 Na2SO4 2 CH3COOH no precipitate. Draw the products formed in each reaction. AB CD AD CB metathesis now the trouble i have is not in balancing the equation but figuring out what the out come of the reactants will be.
For each reaction calculate the mass in grams of the product formed when 106 g. ___CH 4 ___O 2 ___ C 4H 10 ___ O 2. A double-replacement reaction is when the ions in two compounds exchange places with each other in an aqueous solution.
AA bB cC dD where A and B are the reactants and C and D are the products and abc and d are the coefficients the rate of reaction between the substances are relative to each other and the relationship is linked via the stoichiometric ratio. Most precipitates are formed in a double-replacement reaction. Problem 23 Medium Difficulty.
The mole ratio between H 2 and H 2 O is 1 mol H 2 1 mol H 2 O The mole ratio between O 2 and H 2 O is 1 mol O 2 2 mol H 2 O The molar masses of each reactant and product are also needed. Assume there is more. For each reaction specified in Problem 22 determine the amount in moles of excess reactant that remains.
A B AB combination b. For example to determine the number of moles of water produced from 2 mol O 2 the balanced chemical reaction should be written out. ___ CO 2 ___ H 2O ___ CO 2 ___ H 2O 2 2 2 13 8 10.
AX BY. Given a reaction equation. B When the reaction proceeds O-H absorption at 3600 3200 c m 1 diminishes and the product shows C O absorption at 1750 c m 1.
Key Takeaways Key Points Molar ratios state the proportions of reactants and products that are used and formed in a chemical reaction. AWhen the reaction precedes the C c absorption at 1650 c m 1 diminishes and the product shows only C s p 3 H absorption at 3000 2850 c m 1. 2KsCl2gâ â â â â â 2KCls Part B.
If no reaction occurs label the reaction with no reaction. The right side of a chemical equation shows the products created by the reaction. The insoluble salt that falls out of solution is known as the precipitate hence the reactions name.
AB C CB A substitution d. Then balance the equation can be tricky.

Crossed Claisen Reaction May Give A Mixture Of Products Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Reactions
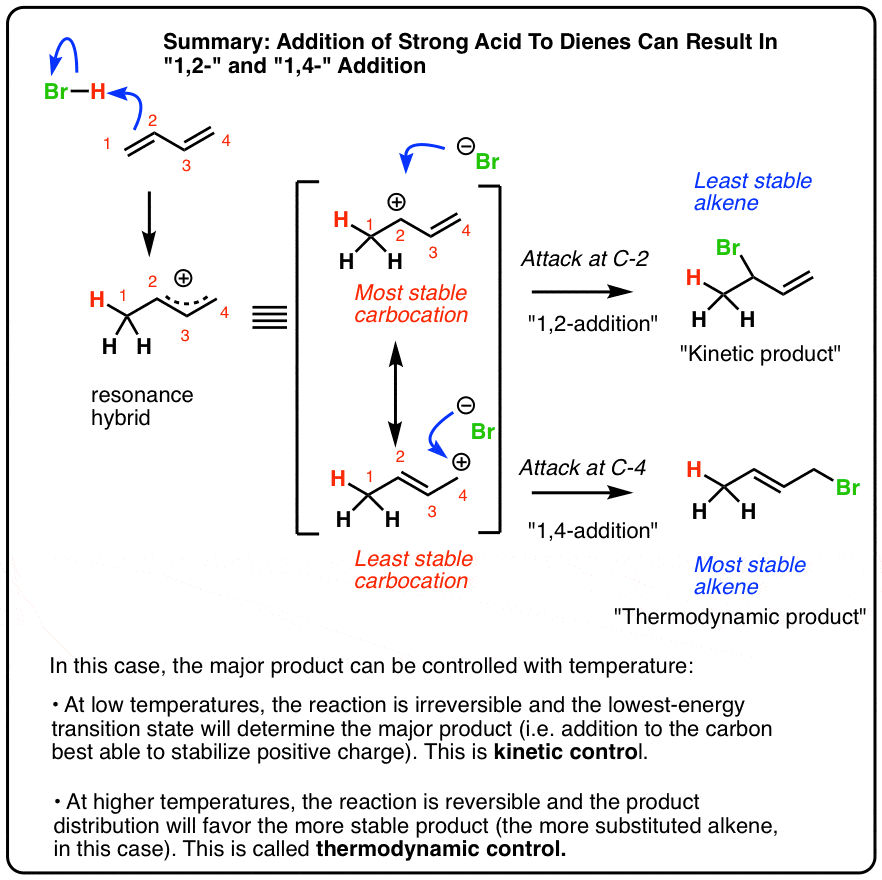
Reactions Of Dienes 1 2 And 1 4 Addition Master Organic Chemistry
Calculating The Amount Of Product Formed From A Limiting Reactant Worked Example Video Khan Academy

Enolate Alkylation Practice Problems Chemistry Organic Chemistry Practice

Claisen Condensation Practice Problems Chemistry Organic Chemistry Condensation Reaction

Organic Chemistry 5th Edition Textbook Solutions Chegg Com Organic Chemistry Textbook Chemistry

Calculating Amounts Of Reactants And Products Worked Example Video Khan Academy


0 Response to "Determine the Products Formed in Each Reaction"
Post a Comment